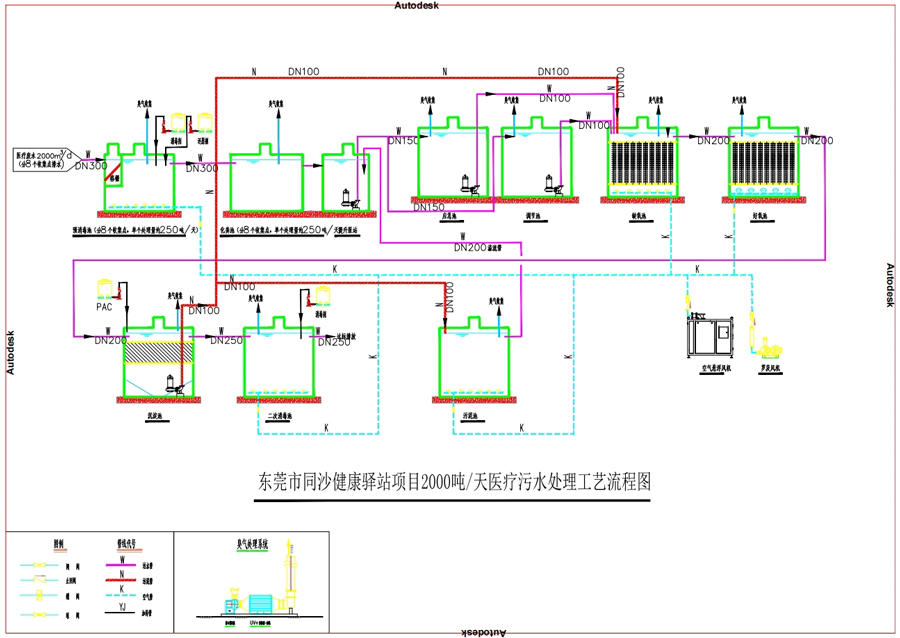
Sewage treatment scale: Calculated based on 5000 isolated beds and 1000 medical staff, the sewage discharge volume is considered, taking into account flushing and other water volume. The design water volume is 2000m 3/d
The medical waste water is collected by the pipe network and then enters the pre disinfection tank in each area. Sodium hypochlorite is added in the pre disinfection tank to preliminarily disinfection and sterilization the bacteria and viruses in the water, and then the reducing agent is added in the rear section of the pre disinfection tank to remove the chloride in the water and then enters the septic tanks in each area. The effluent from the septic tanks in each area enters the lift pump station through the pipe network and is lifted to the regulating tank by the lift pump of the lift pump of the lift pump station (in case of emergency, the valve can be controlled to lift to the emergency tank, and then the lift pump of the emergency tank can be started to lift to the regulating tank for a series of treatment after the water quality and quantity are adjusted in the regulating tank, and then the lift pump of the regulating tank is used to lift to enter the anoxic tank, where anoxic reaction is carried out. It can decompose macromolecular organic matter into small molecular matter, improve the biodegradability of sewage, and ensure the effect of subsequent biochemical treatment; At the same time, the filling layer plays a strong role in intercepting water and has a good effect on removing SS from the water body;
After being treated in the anoxic tank, the wastewater enters the aerobic tank, where an aeration device is installed for continuous aeration. Under the action of aerobic bacteria, most of the remaining BOD5 in the wastewater can be degraded into CO2 and H2O, and ammonia nitrogen can be converted into nitrate nitrogen, which plays a major role in the degradation of COD and ammonia nitrogen.
The effluent from the aerobic tank enters the sedimentation tank, where the suspended solids in the water are intercepted, and the clean water flows into the secondary disinfection tank automatically. Sufficient disinfectant is added in the tank, and enough contact time is ensured to completely disinfection and sterilization the bacteria in the water, and finally discharge up to the standard.
After entering the sludge tank, disinfectant is added for disinfection and sterilization, and then transported to a medical waste treatment facility for disposal.
Water quality discharge standards
The treated water quality meets the requirements of the "Water Quality Standards for Sewage Discharged into Urban Sewers" GB/T31962-2015 and the "Emission Limits for Water Pollutants" DB44/26-2001. Please refer to the table below for details.
序號 | 污染物名稱 | 單位 | 排放濃度限值 | 備注 |
1 | pH | ---- | 6-9 | |
2 | 腸道致病菌 | 個(gè)/L | 不得檢出 | |
3 | 腸道病毒 | 個(gè)/L | 不得檢出 | |
4 | 結(jié)核桿菌 | 個(gè)/L | 不得檢出 | |
5 | 色度 | 稀釋倍數(shù) | ≤30 | |
6 | 糞大腸菌群 | 個(gè)/L | ≤100 | |
7 | 余氯 | mg/L | 6.5-10 | |
8 | 氨氮NH4-N | mg/L | ≤15 | |
9 | 化學(xué)需氧量CODCr | mg/L | ≤60 | |
10 | 生化需氧量BOD5 | mg/L | ≤20 | |
11 | SS | mg/L | ≤20 | |
12 | 動植物油 | mg/L | ≤5 | |
13 | 石油類 | mg/L | ≤5 | |
14 | 陰離子表面活性劑 | mg/L | ≤5 |
Process flowchart